 ber
tells you the number of neutrons.
ber
tells you the number of neutrons.End-of-Course Test Study Guide Part 3 of 7 (15% of Final Average!!!!)
Content Domain 3: Chemical Basis of Life
1. Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. The 3 states are solid, liquid, and gas.
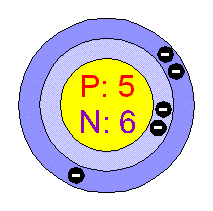
2. The atom is the building block of all matter. There are 3 particles. Inside the nucleus are the protons, which have a positive charge, and the neutrons, which have no charge. Surrounding the nucleus are the negatively-charged electrons.
3. Electrons found in the outermost shell are called valence electrons. When this shell is full, the atom is stable and does not bond with others. There can only be w electrons in the first shell, 8 in the second shell, and 8 or 18 in the third shell.
4.
The atomic number tells you the number of protons,
which equals the number of electrons in a neutral
atom. The atomic mass minus atomic num ber
tells you the number of neutrons.
ber
tells you the number of neutrons.
5.
![]() Draw
the atomic structure for boron.
Draw
the atomic structure for boron.
6. An element is a substance made up of all the same kind of atoms. The most common ones found in living things are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus.
7. There are 3 types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, and hydrogen.
a. ionic bond: electrons are transferred, resulting in charged atoms that are held together because opposites attract. Ex- NaCl (sodium chloride)
b. covalent bond: electrons are shared. Ex- CO2
c. hydrogen bond: weak attractions between polar molecules. Ex- holds water molecules to other water molecules; holds nitrogenous bases together in a DNA molecule
8. A chemical reaction is when chemical bonds are broken and new bonds form.
9. An organic compound always contains carbon and comes from living things.
10. An inorganic compound does not contain carbon and comes from nonliving things.
11. The most important inorganic compound for living things is water. It is polar (the hydrogen side is positive while the oxygen side is negative). It is a great solvent (it can dissolve most things), necessary for most chemical reactions in living things.
12. The pH scale, from 0 to 14, is a measure of how acidic or basic something is. Neutral is 7. Acids are less than 7. Acids release hydrogen ions (H+). Bases are more than 7. Bases release hydroxide ions (OH-). Stronger acids and bases are farther from 7, while weaker acids and bases are closer to 7.
13. The four basic types of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
14. Carbohydrates contain these 3 elements: C, H, and O. Carbs provide a major source of energy. Monosaccharide example: glucose polysacchararide example: starch and cellulose
15. Three types of lipids are fats, oils, and waxes. The building blocks of lipids are 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains. Uses in the body: insulation; waterproof skin (& plant leaves); cover neurons to insulate current; found in phospholipid membranes
16. Proteins contain these elements: C, H, O, N, and sometimes P. The building blocks are amino acids. They are used for growth and repair. A special type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction is called an enzyme.
17. Nucleic acids contain an organismís genetic code. The building blocks are nucleotides. Ex: DNA & RNA
18. When cells break down glucose to make energy, they are carrying out cellular respiration. Plants get this food by performing photosynthesis.
19. Write the balanced chemical equation for cellular respiration: Circle the reactants, underline the products. C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6H2O + 6CO2
20. Write the balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis: Circle the reactants, underline the products. 6H2O + 6CO2→C6H12O6 + 6O2
21. The molecule that cells use to carry out cellular activities is called ATP. Energy is released when one phosphate is removed, forming ADP.
22. What is the ultimate source of energy for all living things? sunlight
23. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? aerobic uses oxygen; anaerobic does not
24. What are the 2 types of anaerobic respiration? lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation How many net ATPs are produced in each? 2 How many net ATPs are produced in aerobic respiration? 36
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation
25. What 3 things make up a nucleotide? phosphate, 5-carbon sugar, nitrogenous base
26. How do the nitrogenous bases pair up? A-T, C-G
27. What is it called when DNA is copied? replication Where does it take place? nucleus
28. What would the complementary strand of DNA look like for: A T T C G C A T G? T A A G C G T A C
29. Name 3 ways that DNA and RNA differ. DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose; DNA is double-stranded, RNA is single-stranded; DNA has thymine; RNA has uracil
30. What are the 3 types of RNA and what do they do? mRNA- brings copy of instructions from DNA in nucleus to the ribosomes; rRNA- along with proteins, makes up ribosomes; tRNA- brings amino acids to the ribosome to build proteins
31. What is it called when DNA is used to make mRNA? transcription
32. Transcribe the following A T T C G C A T G U A A G C G U A C
33. Three bases in a row make up a codon. This matches to the anticodon found on the tRNA. The tRNA carries the appropriate amino acid to build a protein. This occurs at the ribosomes. The process is called protein synthesis, or translation.
34. What shape does a DNA molecule have? double helix