Lab Activity 16.2 - VSEPR Theory
Purpose: To use Lewis dot
structures to predict the geometry of a molecule from the Valence Shell
Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model.
Materials:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Procedure:
VSEPR Tutorial: http://wblrd.sk.ca/~chem20bb/covmolec/vseprmovie.html
- Go to the website above and work through the tutorial.
- You will be asked to build molecules using styrofoam balls and the toothpicks. Replace the styrofoam balls with balls of Play-Doh. Each molecule that you build will contain the large Play-Doh ball as the central atom in the molecule. Please actually build each model so that you can see the model in three-dimensions. Verify the angles between atoms with a protractor.
- As you build your molecules, record the entries in Table 1. Remember that the electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule will repel each other and move as far apart as is possible.
- Use your VSEPR chart to work through the examples in Table 2 and predict the geometry of the given molecules. Check your answers using the tutorial.
Molecular Origami
- On the origami models, use a marker to draw color
coded circles over each of the chemical symbols of the atoms. You are doing this because some of them
will be cut off when you cut out the patterns. Use this color scheme: C – black, Cl
– green, F – purple, S – yellow, P – red, H - blue
- Cut out the origami models. Hold the paper with the print side up – we’ll call this the front and the non-printed side the back. Fold along the lines. On a solid line, fold towards the back. On a dotted line, fold towards the front. Make sharp creases and corners. Tape or glue your models together.
- Describe the shape of each of your molecules. Use the shape of the molecule to help draw the Lewis dot structures. Some of these dot structures may be exceptions to the octet rule. Fill in Table 3 as you go.
Table 1 - VSEPR Theory Chart
|
Number of Atoms |
Number of electron pair around the central atom |
Number of lone pair and bonding pair |
Sketch of the molecule |
Bond Angle (Angle between two bonds) |
Molecular Shape |
|
|
LP |
BP |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2 – Examples: Predicting Molecular
Geometry
|
Chemical Formula |
Lewis Dot Structure |
Number of lone pair and bonding pair (count multiple bonds as one pair) |
Molecular Shape |
Bond Angle (Angle between two bonds) |
|
|
LP |
BP |
||||
|
H20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NH3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CO2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
HBr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PF5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SO2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CH4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BeCl2 |
|
|
|
|
|
Table 3 – Molecular Origami
|
Chemical Formula |
Molecular Shape |
Lewis Dot Structure |
Number of lone pairs and bonding pairs |
|
|
LP |
BP |
|||
|
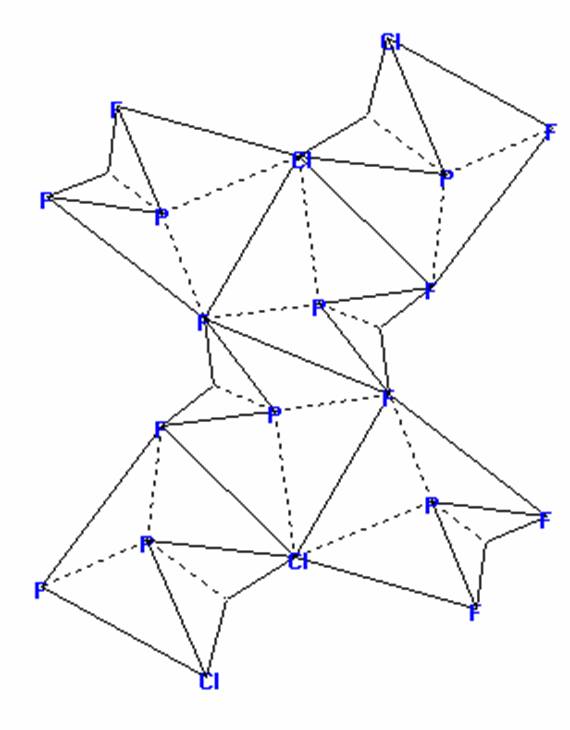
PCl2F3 |
|
|
|
|
|
CCl2F2 |
|
|
|
|
|
SF6 |
|
|
|
|
|
PHF2 |
|
|
|
|
Conclusions and
questions:
1) In a trigonal pyramidal molecule, why are the angles less than 109.5o?
2) When would a bent molecule have bonds of less than
a) 120o?
b) 109.5o?
3) Which of your “origami” molecules were exceptions to the octet rule?
4) Look at your origami model of CCl2F2. Give some reasons why the shape of this molecule is not a regular tetrahedron (all sides equal, all angles equal to 109.5o).
5) Consider the ammonium ion, NH4+.
a) Draw the Lewis dot structure.
b) What is its molecular shape?
c) What are the bond angles?
d) How is this like and unlike the CCl2F2 molecule?
6) Draw the Lewis Dot structure and give the molecular shape and the bond angle(s) for each of the following:
|
a) CO molecular shape: bond angle(s): |
b) H2S molecular shape: bond angle(s): |
|
c) CCl4 molecular shape: bond angle(s): |
d) CH2Cl2 molecular shape: bond angle(s): |
|
e) SiF62- molecular shape: bond angle(s): |
f) AsF3 molecular shape: bond angle(s): |
Molecular
Origami
phosphorus dichloride trifluoride
PCl2F3
dichlorodifluoromethane
CCl2F2

sulfur hexafluoride
SF6

difluorophosphine
PHF2
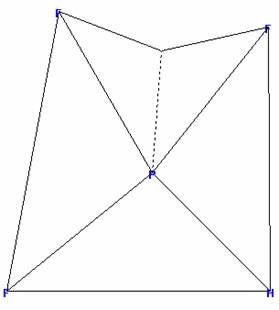
Please note that the origami models in
this packet are not all to the same scale.