Ken Szulczyk's Lecture Notes for Environmental and Natural Resource Economics
Lectures #3 and #4 - Property Rights and Market Failure
Private Property Rights
- Property rights—a bundle of entitlements
- Describe an owner’s rights, privileges and limitations for use of a
resource.
- Government restricts use of private property
- Example - land
- You own land in a neighborhood of one-story houses
- Zoning laws -
- You cannot build a factory there
- You cannot build a 40-story skyscraper
- Conflict between Government and the Public
- Endangered Species Act: - A U.S. federal law that protect
threatened and endangered species by preserving their environment
- 5th Amendment to the Constitution - Government cannot take land
without compensating the land owners
- If government finds an endangered species living on your
property, then
- Owner has severe restrictions on their property
- The government took the property, because it severely
limited the owners choices
- Government does not compensate to protect endangered species
- Private property regimes - individuals hold entitlement
- State-property regimes - governments own and control property.
- Common-property regimes - property is jointly owned and managed by a specific group.
- They can exclude outsiders
- Open access regimes - no one owns or exercises control over the resources.
Markets
- Markets - bring buyers and sellers together
- Creates harmony
- Adam Smith - coined the phrase "The Invisible Hand"
- Free market of individuals acting in their own self interest
leads to a socially-desirable result.
- Market price communicates information to market participants
- If price is high, then suppliers could be earning profits
- if suppliers are earning profits, then they should expand
production
- If price is low, then suppliers could be earning losses
- if suppliers are earning loses, then they should contract
production
- Profits and market prices direct resources to the most
profitable industries
- Market requires many assumptions
- Large number of buyers and sellers
- Thus, market has the maximum social welfare
- Both consumers' and producer's surpluses are maximized
- Market price is $1.50

- Market failure - something prevents the market to allocate resources
efficiently
- Example
- If a market has one buyer (i.e. monopsonist), then the buyer
dictates the market price
- Walmart - the largest corporation in the United States
strong arms its suppliers
- If a market has one seller (i.e. monopolist), then the seller
dictates the market price
- A market failure implies wastefulness or economic inefficiency
- Graph below shows reduced welfare
- Consumer surplus shrinks
- The demand function determines the market price
- Producer surplus - could expand
- Firms still in the market are selling for a higher price
- Black triangle - Deadweight loss to market
- Trade has been reduced

- Transaction costs - costs involved in making a transaction.
- High transaction costs could prevent trade
- Include
- Search and information
- Bargaining and decision
- Monitoring and enforcement
- Transportation and setup
- Example - land transfers in the United States have high transaction
costs
- From 3% to 9% of value
- A $100,000 house could have transaction costs up to $9,000
- New York Stock Exchange has high setup costs, but once market is
operating tends to be low cost.
- Financial instruments are uniform and many
participants
Private goods - goods supplied by producers in private sector
- Characteristics
- Rivalry - if one person buys and consumes a product, then another cannot buy
and consume that product
- If a person buys and drinks a Coca-cola, then another customer cannot consume
that Coca-cola.
- Excludable - producers can restrict consumption of their product to consumers
who paid for it.
- A store can restrict its sell of Coca-cola to a paying customers.
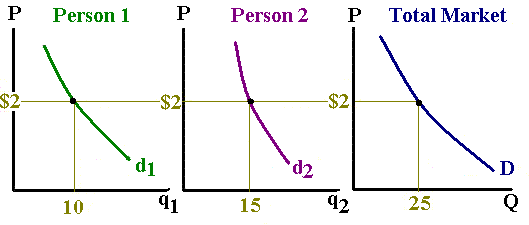
- Two people are in the market.
- Each person has their demand function.
- The quantity denoted by q is for a person, while Q is the total market
quantity.
- Likewise, demand by a consumer is denoted by d, while market demand is D.
- Market demand - at each market price, horizontally sum the quantity that each
consumer buys.
Market Failures
1. Public Goods - the market under supplies public goods and over supplies
public bads, like pollution (Knut Wicksell 1896).
- Two conditions
- Non-rival – one person consuming and enjoying a good does not prevent another
person from consuming that good.
- Non-excludable – no person can be excluded from consuming that good.
- Free riders will consume public good, but not help pay for it
- Examples:
- National defense (military)
- Radio and television broadcast signals (FCC)
- Clean air (EPA)
- Stable monetary and financial environment
- Central bank - influences inflation, interest,
and foreign exchange rates
-
Examples
-
Air Pollution
-
Non-rival - one person or firm polluting the air does not prevent another
from polluting the air
-
Non-excludable - difficult to prevent people from polluting the air
-
Global Warming
-
Substitute greenhouse gases for pollution
- Quasi-public goods - market could supply these goods, but the supply would not
be enough
- Highways
- Libraries
- Education
- Sewage disposal
- Postal service
- Could be perverse market conditions for public goods if supplied by private
market
- Rome had no fire department around 115 B.C.
- Marcus Licinus Crassus - started a private fire department in Rome
- As a person house was burning down, Crassus would be negotiating a price for
his services
- Crassus had market power
- One of the wealthiest Roman citizens
- Lindahl Price - a way to theoretically correct the market failure for public
good
- If we could ask people the price they would be willing to pay for public good
- Then government charges each person his price (i.e. tax)
- However, free riders may not truthfully reveal their preferences or
willingness to pay
- Not practical
- Example
- If government supplies 100 units of a public good
- If people truthfully reveal willingness to pay
- Person A pays $50 for these units
- Person B pays $75 for these units
- Total price is $125 for public good
- "Vertical summation"

2. Asymmetric information - either the buyer or seller has more information
than the other side
- Market may undersupply goods with severe asymmetric information problems
- Examples:
- Credit card companies - calculating interest rates
- Difficult to inspect good or seldom purchases the good from the same producer
- Some firms will provide:
- low-quality
- defective
- even harmful goods
- Moral hazard - one of the parties to a contract change their behavior that
imposes a cost on the other party
- A person gets car insurance and drives more crazy
- A person gets theft insurance for his apartment and he leave the door unlock
- Government insures bank deposits through FDIC
- Banks may lend to more risky borrowers, because their depositors are protected
from deposit insurance.
- Financial institutions may invest in more risky assets, if they are certain
government will bail them out.
- Adverse selection - one of the parties to a transaction withholds critical
information
- Usually people who buy insurance plan to use it
- Person gets health insurance, knowing he has a medical condition
- Person hires an arsonist to burn his business down after getting fire
insurance
- A person buys fire insurance, knowing he faulty wiring in his home
- A person gets a credit card, knowing he will not make payments on it.
- Correcting asymmetric information
- Government
- Some forms may be illegal and prosecuted by government
- Weights and measures - government has inspectors that make sure gas pumps and
supermarket scales are accurate
- Are you sure you if you pumped one gallon and it is truly one gallon
- Government sues producers that make false claims
- Regulations - government approves new products and has inspectors that inspect
products
- Example - USDA has inspectors that frequently inspects meats
- Licenses - ensures professionals have a high level of competency
- Professionals like doctors, lawyers, mechanics, etc. need licenses to practice
- Private market
- Purchasing good regularly
- Brand names
- Franchises
- Product warranties
- Public information - Consumer Reports - magazine that examines consumer
products
- Databases - companies compile information about customers and
payment history
3. Open access property - property owned by society or the absence of
ownership.
- Also called Tragedy of the Commons (Hardin 1968)
- Property rights are not well defined
- Open access is nonexcludable but rivalrous
- Outsiders cannot be excluded from using the property
- Outsiders can consume the resource, leaving nothing behind
- People have less incentive to develop, improve, or maintain land, if others
cannot be excluded from consuming it.
- Examples
- Fishermen over fish in public waters.
- Fishermen catch too many fish, causing
fish populations to decrease to such a level that hurts future fish catching.
- Companies dump wastes onto public lands or waters.
- Air can be an open access resource. Some firms pollute and send pollution into
the air
- Correcting this market failure
- Allow one firm to control the resource
- The firm acts like a monopoly and develops the best plan to
utilize that resource
- Monopoly may abuse that resource too
- Example - monopolist - owns rights to common land with a
forest
- Monopolist cuts down all the trees if lumber prices are
high
- Government create a permit system
- Anyone harvesting or extracting the resource needs a permit
- Common property becomes private property
- Permit holders will monitor the resource against invaders and
poachers
- Government has to monitor the permit holders to ensure they
comply with the terms of the license
4. Externalities - The consumption or production of
one individual or firm affects another person’s utility or production without
their consent.
- The externality influences profits and utility, but does not impact
market prices.
- Key - choice is not incorporated into the market price
- Therefore, an externality is not efficient (Arrow 1969).
(i) Positive externality - an individual's or firm's actions generate benefits for
nonparticipating parties
- The private market may not supply enough
- Supply function understates the true value of output
- S is regular supply function and D is for demand
- Society would desire a higher supply
- Social Marginal Costs (SMC) - the marginal cost function that is
beneficial for the whole society

- Example 1 - Inoculation for diseases
- Each person who gets an inoculation can prevent spread of a disease
- Example 2 - scientific knowledge or technological know-how
- Fixing positive externality
- Subsidies - government provides subsidies so producers will supply more
- Example - government grants subsidies to producers of vaccines
- Note - government could subsidize the consumer to take advantage of the
externality
- Government provides the good
- Health departments give vaccines to the poor and elderly
- Government provides legal protection
- Patent - grants inventors exclusive right to producer their
invention for 17 years in the United States
- Some countries may not honor patents
(ii) Negative externality - an individual's or firm's choice or action
negatively harms
others without their consent
- Property rights are not defined well
- Not all costs are registered, therefore supply function understates the true
cost of production
- Example: A firm emitting pollution will typically not take into
account the costs that its pollution imposes on others.
- Market price is too low
- Market quantity is too high
- The goal is to have firms pay for pollution
- The goal is not to set the pollution to zero!
- The pollution is in excess of the 'socially efficient' level.

- Correcting this market failure
- Have a large list in next section
- If negative externality is between two firms, gov. could be possible
to merge both firms
together
- Not likely
- Government seizure of property or aiding the growth of a
monopoly
Fixing Negative Externalities, like Pollution
Also works for some open-access sources and some types of public goods
1. Prohibit or outlaw the pollution
- Government makes the pollution illegal or shuts down industry
- Problems
- Creates job losses as industry shuts down.
- If industry that generates pollution has a strong demand, then black
markets could develop.
- Government spends money to monitor, arrest, and incarcerate
violators
- Industry relocates to another country and exports it back to the
original country
2. Lawsuits - U.S. has a variety of laws that allow people to sue to
address externalities
- If firms know that they are creating negative externalities, they reduce
negative externalities to reduce likelihood of being sued
- Firms compare marginal abatement cost to the marginal damage
- By avoiding damage, the firm lowers its liability
- Damage to the environment is very hard to estimate.
- Note that the government does not need to know the marginal costs of the firm
in order to achieve the desired level of pollution.
- Problems
- The burden of proof may be difficult in court.
- Litigation is costly
- Large legal fees and damage awards
- Need to know both who causes the harm and what the damages are.
- Courts are slow
- Renting seeking behavior – encourage attorneys to sue for large
legal fees and damage awards
- Leakages – manufacturing firms may flee to developing countries with
weak environmental laws
- Courts usually do not come up with comprehensive plans
- Rules are developed from a case-to-case basis
3. Command-and-control regulations (CAC) - government uses laws and regulations that
dictate the standards and/or technology used to reduce pollution.
- Government fines and penalizes companies that violate the rules.
- Government could permanently shut down a company for
excessive violations
- U.S. has historically used command and control (CAC) policies
- Why, when market-based environmental policies are more efficient?
- Reasons
- Environmental groups - firms shouldn't be able to buy the right to
pollute
- Immoral to hurt the environment
- Politicians prefer CAC because:
- Many are trained as lawyers.
- Created laws and regulations are their jobs
- The costs of CAC are less
obvious
- The private firms bear most the costs
- All firms are treated fairly
(i) Types of command and control regulations
- Ambient Standards - Regulates the
amount of pollutant present in the surrounding (ambient) environment.
- Government has sensors the measure pollution levels in an area
- Examples:
- Parts per million (ppm) of dissolved oxygen in a river
- Sulfur
dioxide (SO2) in an airshed
- Measures are often an average over a 24 hour period or per year
- Concentrations vary by time of day and by season (e.g. due to changes in
weather)
- Note that the level itself cannot be directly enforced
- Government tracks down the suspects, i.e. the polluting firms
- The firms have to develop a plan to reduce pollution
- Emission standards - regulates the level of emissions allowed
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has links to sensors in
electric power plants in the United States
- The polluter may have freedom to choose the technology used
- Examples
- Emissions rates (pounds of SO2 per hour)
- Technology standards - require polluters to
use certain technologies, practices, or techniques.
- Examples
- Before 1990, electric utilities were required
to install scrubbers with 90% efficiency ratings.
- Coal has trace amounts of sulfur
- The scrubbers removed SO2 from the exhaust
- U.S. gov. requires catalytic converters in automobiles with gasoline
- Converts have platinum, which is expensive
- Reduces NOX emissions
- Oxides of Nitrogen, such as nitrous oxide (N2O) and nitrogen
oxide (NO)
(ii) Grandfathering of regulations- standards and regulations depend on the
date the company starting using specific machines and equipment
- The date a electric power plant started operating
- Newer units face more
restrictive regulations.
- Older units are often exempt, i.e. grandfathered.
- Grandfathering reduces resistance to the new regulations
- Easier to pass regulations if they do not harm existing firms
- Could lead to more emissions in the short run
- Companies use the older, less efficient equipment longer
- New technology may be expensive
- Firms may reduce investment in new technologies or renovated an old
plant or factory
- If a firm upgrade or renovates its facilities, then the new regulations apply
- Potential
for economic rent for existing firms
- rent - unfair, long-run profits
- firms with old equipment may have a cost advantage
- New firms may not enter the market
- Creates a barrier to entry
- Higher investment costs to implement that regulations
(iii) Problems with command and control regulations
- Not efficient
- Freezes technology and limits firm’s flexibility
- U.S. government uses self-monitoring
- Firms keep their own records on emissions, and are subject to surprise
audits.
- Although regulations are set by the federal level, the local governments
enforce the regulations.
- Local government may be more concerned about creating jobs and
expanding the tax base
4. Coase Theorem - disputing parties will work out a private agreement that
is efficient
- Named after Noble laureate Ronald Coase (1960)
- Externalities are reciprocal in nature
- Not only does the pollution cause
an externality, but also the presence of the victims harms the polluter
- Pollution is not a problem if no one were harmed
- Polluting firms and the people that are harmed by the pollution can negotiate
to reduce pollution.
- Does not depend which party holds the property right.
- Example - a firm dumps pollution into a lake that kills the fish.
- If the right to use the lake is given to the fishermen, then the polluting
firm has to negotiate and compensate fisherman in order to pollute the lake
- If the right is given to the polluting firm, then the fishermen will pay the
firm not to pollute the lake.
- Benefits
- Could work for small group of people
- Private parties solve a pollution problem without the government’s
help
- Assumptions and Problems
- Property rights are well defined
- Someone owns the resource
- Need to be able to clearly establish who causes the harm.
- Some victims aren't well defined (e.g. endangered species)
- Zero transaction costs
- Search and information
- Bargaining and decision
- Monitoring and enforcing
- Perfect information
- A court system enforces contracts without any costs.
- Two parties (it is more difficult for large groups of people to agree about
something).
- No wealth effects.
- If ownership of the resource makes one party wealthier, then that party may
be more resistant to bargaining.
- More people will come to the problem if they are likely to be
compensated.
5. Market incentives - government uses price or quantity mechanisms to
internalize the externalities.
- Price incentives
- Pollution taxes - government puts a price on pollution
- Subsidies - government helps firms pay for pollution equipment
- Quantity rationing
- Market permits - government requires firms to have a permit in order
to pollute
- Government creates permits
- Firms may purchase or sell permits in a market
(i) Pigouvian Taxes - government places a tax directly on pollution.
- Government imposes a tax for each unit of pollution that is emitted
- Firms are supply too many units to the market
- Government places a tax on pollution
- Taxes increase a firm's costs and reduces profits
- The Pigouvian tax works by internalizing the cost of the
externality.
- Polluter incorporates the social cost of pollution.
- Firms also have an incentive to develop new pollution control
technology in order to avoid paying taxes
- Government implements a tax on pollution, which puts a price on
pollution
- Equilibrium price increases while quantity supplied decreases
- This is efficient because firm pays all costs including pollution
- Firms still pollute, but less
- Firms can pay the tax on pollution or avoid the tax by reducing pollution

- Welfare effects
- Usually taxes cause a deadweight loss on society
- However, firms are polluting, which is harming the environment
- It is like the environment is subsidizing the production
- Shown in graph below
- Red triangle - shows up as consumer and producer surpluses, but
represents damage to the environment
- Price is too low and quantity is too high
- Yellow triangle - damage to environment; nobody benefits from
this
- Quantity should be less than Q*
- It is not the price that damages the environment, but the
quantity

- Alternative method to show tax
- Be careful of the scale
- MB - as firms invest in more abatement equipment, the marginal
benefits to the environment decreases
- MC - as firms invest in more abatement equipment, its marginal costs
increase
- Gov. places a tax on pollution
- If there were no tax, firms would not invest in abatement
equipment

- Have to be careful how tax is placed
- If tax is place on any else
other than pollution, then perverse incentives could exist.
- Example 1 - Gov. places tax on coal to reduce sulfur emissions.
- Utilities may use dirtier,
cheaper coal to avoid tax and increase emissions.
- Example 2 - Difficult to measure the actual emissions from cars
- Gov. taxes gasoline, then drivers reduce their mileage
- Gasoline consumption and emission are directly related
- Advantages
- Gives firms more flexibility.
- Firms may meet pollution objective with lower costs
- Problems
- Piguovian taxes require massive
amount of information to implement the tax correctly
- Regressive taxes - placing a tax on an industry makes products more
expensive
- The higher price may impact low-income families, because they
spend more of their income on it.
- Government may be more interested in the tax revenue than setting
the correct tax rate
- Double-dividend debate
- The Pigovian tax causes two things.
- The externality is corrected.
- The tax gives the government revenue, so it could reduce other distortionary taxes.
- Taxes distort markets, because market prices are higher and market quantities
are lower.
- Empirical research indicates Pigovian taxes may also be distortionary
(ii) Government can implement a subsidy
- The opportunity cost of polluting is losing the subsidy.
- Government grants a subsidy to help a firm pay for a specific
abatement technology.
- The technology helps reduce pollution.
- Problems with subsidies
- The polluter receives money from the government, rather than paying
- New firms may enter market, so that total pollution increases
- Need to raise taxes to pay for subsidies
- Taxes create distortions in the market
- Market price is higher and market quantity is lower.
- Ethics - should we have to pay to avoid pollution?
- Subsidies are often politically motivated, and can be difficult to remove
when no longer needed.
(iii) Market Permits - A transferable discharge permit places the maximum limit of pollution or
concentration level that any firm is allowed to discharge into the environment.
- Examples
- Some electric generation plants use coal to generate electricity
- Some coal has sulfur that turns into sulfur dioxide when burned
- Sulfur dioxide leads to acid rain
- They have to buy sulfur dioxide permits
- Proposing a permit system for mercury emission and greenhouse gases
- Government places the maximum amount of pollution that can be emitted
- Also called cap and trade system
- Each polluter has to buy a permit
- One permit allows firm to emit 10 metric tonnes of sulfur dioxide
into atmosphere
- Government creates enough permits, where
- Sum pollution levels in permits = maximum pollution level
- Quantity rationing
- Pigouvian tax - is price rationing
- The permit creates a market price of pollution.
- Firms with high marginal abatement costs buy permits, so that they could
pollute more
- Firms with low marginal abatement costs sell permits, and
pollute less.
- Firms with low abatement costs may be investing in new technology
- Government sets the max. pollution level
- Firm 1 buys permits and pollutes more
- Firm 2 abates pollution and can sell its permits
- Marginal Social Costs (MSC) of pollution
- Q bar is max. pollution level

- Thus, the permit market is efficient, because
- Producers have to keep their pollution level at or below the amount specified
in the permits.
- Used in sulfur dioxide emissions, quotas on fish harvesting, etc.
- Theoretically, you get the same result as a Pigouvian tax
- How are permits allocated
- Government auctions permits - government sells permits to the highest bidder
- Auctioning permits gives government gets revenue from the permits.
- Plan appears as a "tax"
- Grandfathering - government give permits to the firms
- Firms are less likely to resist the implementation of a permit
system.
- How are permits distributed?
- Some firms are bigger than others, etc.
- Distribute permits relatively to their pollution levels
- Hybrid - government could give some of the permits freely and hold some back to
auction off at the market
- Permits require the following to have low transaction costs
- Homogeneous - all permits are identical
- Perfectly divisible
- Exchangeable -producers can buy and sell their permits without
interference
- Market participants - can anyone buy the permits?
- Environmental groups or private individuals could buy permits and retire them
- Pollution is not released into atmosphere
- Benefits
- The permit is a right that can be sold or bought in a market.
- The permit creates a market price for pollution
- Gives firms more flexibility
- Firm may meet objective with lower costs
- Problems
- Regulators must have sufficient knowledge to design the market.
- Government has to monitor pollution levels
- Prevent illegal emissions or illegal dumping.
- Government may have higher enforcement costs
- Market-based policies may lead to localized "hot spots."
- Hot spots - a group of neighboring polluters buy permits to
pollute more
- Concentrated area of pollution
- Does government set a maximum pollution level that applies forever
- Example - no more than 10 trillion tons of sulfur dioxide can be emitted
into atmosphere
- Does government create new permits each year
- The price of market permits can "shoot" up quickly if government
establishes a maximum pollution level forever.
- Hotelling's Rule - Covered in non-renewable resources
- Permit market may have few participants, because it is a specialized
market
- A firm may have market power










