CHAPTER 2 STUDY GUIDE
A hypothesis must have a test for its wrongness to be considered a scientific hypothesis.
Cosmology - a theory of the overall structure and evolution of the universe
Geocentricity - a cosmology theory where the earth is the center of the universe and everything revolves around it
Heliocentricity - the sun is the center of the universe
Direct motion - the planets usual movement to the left relative to the background
Retrograde motion - the reverse movement of the planets relative to the background
What is the historical significance of retrograde motion?
Specifically who were Ptolemy, Aristarchus, Copernicus, Brahe, Kepler, Galileo, and Newton? What was their individual significance to Astronomy?
Ptolemy - a Greek astronomer in Alexandria, Egypt, who made a geocentric theory about retrograde motion of the planets. Each planet moved in a small circle called an epicycle, the center of which moves in a larger circle called a deferent whose center is offset from the Earth.

Aristarchus - a Greek astronomer who proposed a heliocentric theory on retrograde motion that the planets revolve around the sun and that Mars appears to have retrograde motion because the faster-moving Earth overtakes and passes the red planet.
Copernicus - a Polish astronomer who developed a heliocentric theory of the known universe and published his work in 1543. He eventually concluded that the orbits of Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn lie outside the Earth’s orbit.
Brahe - a Danish noble who developed a cosmology wherein the earth stood still, the sun and moon revolve red around it, and the other planets revolved around the sun.
Kepler - a German astronomer who developed three laws explaining the cosmos that he deduced from Brahe’s observations
Galileo - an Italian astronomer that turned his telescope skyward and made observations that supported the heliocentric cosmology
Newton - an English astronomer who built a reflecting telescopes and made great observations about the nature of light and color
Where are the planets when they are in inferior conjunction, superior conjunction (which planets, too), opposition, and conjunction?
When Mercury or Venus are between the earth and sun, they are in inferior conjunction
When either Mercury or Venus are on the opposite side of the sun from the earth, they are in superior conjunction.
When any of the outer planets are on the opposite side of the sun from the earth, they are in conjunction.
When any of the outer planets are on the opposite side of the earth from the sun they are in opposition.
Why are Mercury and Venus called morning and evening stars? What creates this phenomenon?
They are called morning and evening stars because they are only seen in the morning when the sun is rising or in the evening when the sun is setting.
This phenomenon occurs because Mercury and Venus are between the earth and the sun so their angle in the sky is never much more than the angle of the sun.
What are Kepler’s 3 laws?
1. The orbit of a planet about the sun is an ellipse with the sun at one focus.
2. A line joining a planet and the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals if time
3. The square of a planets sidereal period around the sun is directly proportional to the cube of the length of its orbit’s semi-major axis
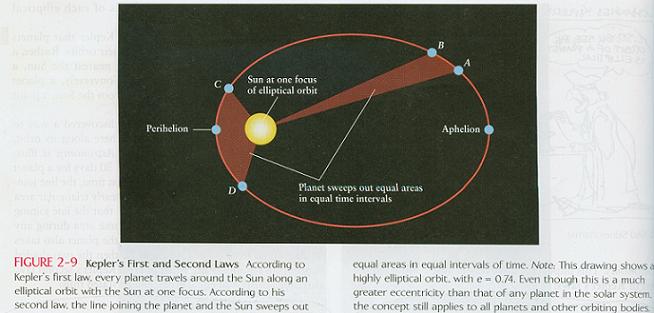
Where are the locations of aphelion and perihelion?
Aphelion is the place in a planet’s orbit when it is farthest from the sun.
Perihelion is the place in a planet’s orbit when it is closest to the sun.
What is an AU?
An AU is an Astronomical Unit that is equal to the average distance between the Earth and the Sun
Galileo was the first to turn the telescope skyward. What 4 observations is he credited with? Besides being the first, what is their historical significance?
Galileo discovered 4 of Jupiter’s moons. This discovery provided proof that the Earth is not at the center of the universe, and that the Earth orbits the sun just like the other planets in our solar system.
Newton’s description of what gave foundation for the heliocentric theory and Kepler’s three laws?
Newton’s law of gravity could mathematically explain Kepler‘s three laws.
How and why was the planet Neptune discovered?
After the discovery of Uranus, it was proven that the planet was not following the orbit predicted by Newton’s laws. Neptune was predicted to exist because that was the only way Uranus’ behavior could be explained. It was found less than 1° from its predicted position





