
To see a square bubble, cartoons, fossils and other odds and sodds click the home button
The Three States of Matter
and
How charges are separated
|
Note:
The following is theoretical, not fact. |
 |
 |
 |
| In it's solid state matter shares the most electrons It is this sharing of electrons by molecules that holds the atomic structure together and gives matter it's solid characteristics. Temperature and pressure determine how many electrons will be shared. | In the liquid state matter shares fewer electrons and it's molecules are more loosely bound together. There are not enough molecules sharing electrons to enable the substance to hold any kind of shape. |
In the gas state matter does not share electrons. Each molecule has it's own valance electrons and is therefore not bound at all to it's neighbors. It can move about independently . |
|
Lets imagine that it instead of
the electrons storing the heat energy of an atom the energy is
stored in the time space continuum between the orbitals much like the
electrons in a capacitor are stored on the dielectric plates
of a capacitor, (not on
the conductor as many people assume.) As more energy is absorbed into
the time space continuum the space expands pushing the orbits out and
increasing their diameter. As the Valance band gets larger in diameter
it increases the number of electrons it can support . So as liquid
water gains more heat the pressure bands between the orbitals expand
pushing the valance band outward, increasing it's circumference and
allowing it to be able to support eight electrons instead of seven and
a
half or seven and sharing the eighth. As we travel toward the center of
the atom the orbitals become more stable the closer we get to the
nucleus. This is because the outer pressure zones squeeze the inner
zones so the further we go toward the center the more pressure there is
being exerted from the outer zones. This makes the inner orbits very
stable and makes it very hard for electrons to jump between
orbits. These pressure bands are affected by heat energy
which they absorb creating more pressure and forcing the electrons to
move further from the nucleus. If we picture an atom the size of a
football stadium, with the electrons orbiting around the upper deck,
the nucleus at midfield would be about the size of a quarter. So you
see there is plenty of storage space for energy between the infield and
the upper decks. We know that energy is stored by atoms some place. The
electron is too small to store enough energy and for that matter so is
the nucleus. So where else could it be stored? There is only one
logical explanation. It is stored in the massive area between the
orbitals.
What
I am proposing then is that the amount of heat energy stored in the
energy fields between
the electron orbitals is proportional to the sizes or diameters of the
orbits and the number of electrons orbiting outside the pressure band
or energy field.
It
is the density of the energy field between orbitals that governs the
diameter of the orbitals of
electrons and conversely the number of electron orbits on the outer
side the pressure zones determines the pressure or compression of each
pressure zone or energy field.
|
|
An atom depicting orbitals and energy fields. As one goes further towards the nucleus the Pressure of each progressive energy field or pressure zone increase proportional to the number of outer electron orbits. |
Why is a battery
like a thunder storm?
| The apparatus that produces lightning is simply a huge battery or galvanic cell here after referred to as a battery. You will notice a change in normal terminology as the battery is described here. If we construct a battery with a copper cathode and a zinc anode we would see that cations, (positive), in the solution evaporate into the solution from the zinc anode and on the other side copper anions, (negative), condense from the solution onto the cathode . The current is conducted from the evaporation on the anode to the meter and then to the cathode where condensation carries it into the solution again. This is the very same direction current travels in a thunderstorm. from evaporation electrons travel to the sky where condensation releases them in the clouds and when the release is rapid enough and in enough volume lightning returns them back to the earth again. | 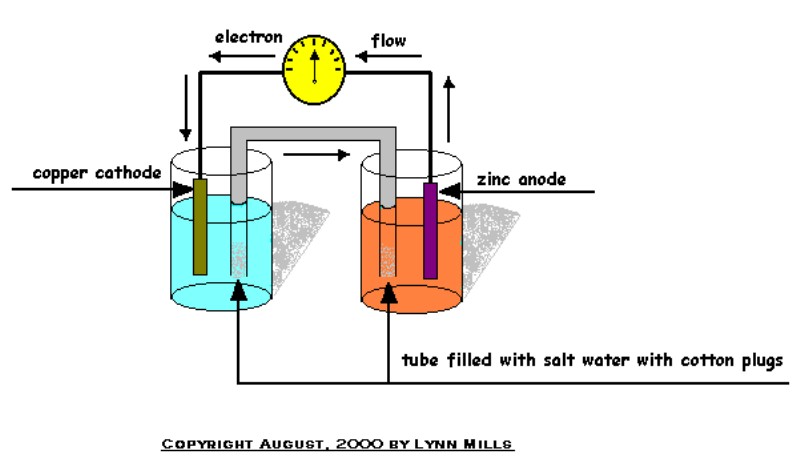 |
| If we simplify the battery and then tip it on end we can see the analogy a little better. The Zinc anode represents the oceans and the copper cathode represents the clouds. The solution is the atmosphere. The porous barrier is not important to this discussion and is only placed in the graphic for accuracy. Evaporation occurs from the zinc, (ocean) and carries the electrons to the solution, (atmosphere), where it condenses on the copper, (into clouds) from there it completes the circuit through the solution, (atmosphere) to the zinc, (via lightning to the earth). The more active a metal or substance is the more electrons are released by matter state change. It is matter state change, solid to liquid, liquid to gas, and visa versa that creates charge separation in batteries and in thunderstorms. |
|
Email wwindmills@comcast.net